Diet and Nutrition
» Dietary Management in General
Getting started to develope healthier eating habits, get more active and get on track to start losing weight.
Our Weight loss guide features :
- We concentrate on weight loss with scientific approach with individual diet for individual person
- Promotes safe and sustainable weight loss
- Learn to make healthier food choices
- Get support from our online community
- Learn skills to prevent weight regain
We want to help you adopt a healthier lifestyle so you can lose weight safely and learn the skills you need to keep it off in the long term.
Your calorie allowance on the plan:
- Men should eat and drink no more than 1,900kcal a day.
- Women should eat and drink no more than 1,400kcal a day.
If you normally eat a lot more than the recommended 2,500kcal for a man and 2,000kcal for a woman you may find it hard to cut back to our suggested calorie limit. If so, aim to reduce your calorie intake gradually over the next few weeks.
If people are overweight, it’s usually because they eat and drink more calories than they need.
Losing weight – Getting started is designed to help you lose weight at a safe rate of 0.5kg to 1kg (1lb to 2lb) each 15 to 20 days by sticking to a daily calorie allowance.
For most men, this will mean consuming no more than 1,900kcal a day, and 1,400kcal for most women.
If you go over your limit one day, don’t worry, weve got that covered. It simply means you’ll have to reduce your calorie intake the following days.
For example, if youre a woman and you have 1,700kcal on Tuesday – that’s 300kcal more than your daily calorie allowance of 1,400kcal.
To stay on track, you’ll need to remove 300kcal from your remaining calorie allowance over the rest of the week.
In addition to a healthier diet, regular physical activity along with medication is a vital component of your weight loss journey.
Not only will it help you lose more weight but it will also keep you motivated and improve your general health and well being.
Get off to the best possible start on the weight loss plan with these 12 diet and exercise tips :-
- Don’t skip breakfast
Research shows that eating breakfast helps you control your weight. Some people skip breakfast as they think it will help them loose weight but missing meals doesn’t help us lose weight and isn’t good for us because we can miss out on essential nutrients. It could also encourage us to snack more throughout the day because you feel hungry’. - Eat regular meals
Some people think missing meals will help them lose weight, but it has been shown that eating regularly during the day helps to burn calories at a faster rate as well as reduce the temptation to snack on foods high in fat and sugar. - Eat plenty of fruit and veg
Fruit and veg are low in calories and fat and high in fibre – three essential ingredients for successful weight loss. They also contain plenty of vitamins and minerals. - Get more active
Studies show that regular activity is key to losing weight and keeping it off. As well as providing numerous health benefits, exercise can help burn off the excess calories you cant cut through diet alone. Find an activity you enjoy and are able to fit in to your routine. - Drink plenty of water
People sometimes confuse thirst with hunger. You can end up consuming extra calories when a glass of water is really what you need. You should aim to drink minimum 10 to 15 glass of fluids preferably water or more if it’s warm or you’re exercising. - Eat high-fibre foods
Foods containing lots of fibre will keep you feeling full for longer, which is perfect for losing weight. Fibre is only found in food from plants, such as fruits and vegetables, oats,whole grain bread, brown rice,beans,peas and lentils. - Read food labels
Knowing how to read food labels can help you choose healthier options, and keep a check on the amount of calories, fat, salt and sugars you eat. Use the calorie information to work out how a particular food fits into your daily calorie allowance on the weight loss plan. Find out more about reading food labels. - Use a smaller plate
Studies show that people who use smaller plates tend to eat smaller portions and still be satisfied. By eating with smaller plates and bowls, you may be able to gradually get used to eating smaller portions without going hungry. It takes about 20 minutes for the stomach to tell the brain it’s full, so eat slowly and stop eating before you feel full. - Don’t ban foods
Don’t ban any foods from your weight loss plan, especially the ones you like. Banning foods will only make you crave them more. There’s no reason you can’t enjoy the occasional treat as long as you stay within your daily calories alowens - Dont stock junk food
To avoid temptation, avoid stocking junk food, such as chocolate, biscuits, crisps and sweet fizzy drinks, at home. Instead, stock up on healthy snacks, such as fruit, unsalted rice cakes, oat cakes, unsalted or unsweetened popcorn and fruit juice. - Cut down on alcohol
Did you know a standard glass of wine can contain as many calories as a piece of chocolate, and a pint of lager has about the same calorie count as a packet of crisps? Over time, drinking too much can easily contribute to weight gain. - Plan your meals
Plan your breakfast, lunch, dinner and snacks for the week, making sure you stick to your calorie allowance. Try to plan for four to seven days’ worth of meals and snacks. Make a shopping list, but don’t shop when you’re hungry as that can lead to high-calorie impulse buys!
» Dietary Management for all Diseases
A
ACIDITY OR HEART BURN
| ACIDITY: |
|
Acidity is a common name referred to regurgitation of acid or partly digested food from stomach into food pipe or mouth. |
|
WATER BRASH / HEARTBURN: |
|
Heartburn / water brash is burning sensation behind the breast bone or sternum. It is due to regurgitation of sour fluid from the esophagus into the oral cavity. It is normal when it occurs occasionally but frequent and severe heartburn is a manifestation of some esophageal dysfunction. |
|
PEPTIC ULCER: |
|
Small or big erosion in the mucosa (lining) of the stomach. |
DIETARY MANAGEMENT:-
• Treat the causes- take measures to relieve tensions and stress from life.
• Relax for about 20 minutes before and after eating.
• Eat bland food; less hot food add little or no oil to your food- bland boiled vegetables.
• Eat fresh fruits and salads, ash gourd juice.
• You can have takmaria, commonly known as falooda seeds (Impatiens balsamina), they have cooling effect and helps in digestion in hot weathers.
• Avoid citrus fruits, coffee, tea, raw vegetables, meat extracts, condiments spices and apple.
• Avoid canned and processed food- they contain chemical irritants.
• Avoid fried food and fats – you can include sesame oil, mustard oil, oily fish, linseed oil, skimmed milk and low fat milk products in your diet in small quantities.
• Avoid tobacco and alcohol.
• Eat meals at regular intervals, at regular time.
• Do not overeat; eat small meals at short intervals, little food at every 2 hrs.
• In snacks you can have biscuits (not the cream ones), toast with / without butter, sandwiches, light cake, curds, butter milk, ice creams, custards and puddings.
• Avoid drinking immediately before meals and drink sparingly during the meals.
• Do not exercise, bend, stoop / sleep immediately after meals.
• Avoid drugs like painkillers, antibiotics, aspirin, NSAID, steroids.
• Drink cold milk before retiring to bed.
ACNE
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
AVOID: |
|
• Avoid fats and oily food. |
|
DO: |
|
• Wash your face frequently, at least 5 times a day, taking care that it does not become too dry. |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Drink plenty of water. |
ACUTE RENAL FAILURE [ARF]
Acute renal failure is a clinical syndrome in which there is rapid reduction of the excretory functions of the kidney.
If immediate action is taken derangement caused due to renal failure can be reversed.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Dietary changes are made to correct the fluid and electrolyte imbalance and to maintain proper nutritional status so as to minimize protein catabolism and uraemia. But these dietary changes should be done under guidance of a professional dietician. |
|
AVOID: |
|
• Avoid potassium rich food, as in renal failure potassium excretion is decreased, hence serum potassium level are high which can have deleterious effects on heart. |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Fluid intake is regulated on basis of urinary out put, other water loss from vomiting or diarrhea. Total fluid intake should not exceed – 500 ml + previous day`s urine out put + total water loss from vomiting or diarrhea or any other causes. |
ANGINA PECTORIS
Pain in the region of heart on exertion is known as angina pectoris.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Cut down salt (common table salt) intake in your diet to avoid hypertension. Intake should not exceed more then 2 to 2.5 gm a day. |
APTHOUS ULCER
Small erosions in the oral cavity or on the tongue. They disappear in 7-10 days.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Treat the causes. |
ARTERIOSCLEROSIS OR ATHEROSCLEROSIS
ARTERIOSCLEROSIS / ATHEROSCLEROSIS
Arteriosclerosis is a disease process which is commonly called “hardening of arteries”. It is caused mainly by deposits of calcium and fats on the inner lining of the artery walls which leads to the thickening and loss of elasticity of the artery walls. Eventually there is narrowing of the artery which decreases the blood flow to their respective tissues.
Atherosclerosis is a clot formation in the narrowed arteries and thickening of arteries takes place only in advanced stages or old age.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Avoid foods rich in fats, oils, butter, ghee, nuts etc. |
ASTHMA
It is an episodic chronic respiratory disorder in which there is airflow obstruction causing difficulty in breathing.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Try to recognize and avoid the factors that trigger the asthmatic attacks. |
B
BERIBERI [BERIBERI]
Beriberi is a vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency. There are different types of beriberi – dry (Wernicke-korsakoff syndrome), wet (cardiovascular disease), oriental and infantile.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Increase intake of thiamine (vitamin B1): |
BRONCHITIS [BRONCHITIS]
Inflammation of the large air passages which carry air from the windpipe to lungs is known as bronchitis.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Avoid dairy products like milk, butter, cheese because these will increase mucus secretion in the respiratory system. |
C
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE [CRF]
Chronic renal failure is a progressive or slow continuous destruction of the kidney cells and so kidney is not able to perform its normal function of filtering waste from the blood; as a result the waste remains in the blood.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Dietary changes are made to correct the fluid and electrolyte imbalance and to maintain proper nutritional status so as to minimize protein catabolism and uraemia. But these dietary changes should be done under guidance of a professional dietician. |
|
AVOID: |
|
• Avoid potassium rich food, as in renal failure potassium excretion is decreased, hence serum potassium level are high which can have deleterious effects on heart. |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Fluid intake is regulated on basis of urinary out put, other water loss from vomiting or diarrhea. Total fluid intake should not exceed – 500 ml + previous day`s urine out put + total water loss from vomiting or diarrhea or any other cause. |
CHRONS DISEASE
Chron`s disease is a non-specific granulomatous inflammation involving single or multiple areas of intestine. Most commonly it affects the terminal ileum or the ileocaecal region.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• In acute phase of disease rest and take only liquids- water with salt and sugar, fruit juices- water melon, etc, start dioralyte in case of severe diarrhea. |
COMMON COLD OR CORYZA
COMMON COLD / CORYZA
This is the most common and most frequent viral infection affecting all age groups and is highly contagious.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• In case of profuse water nasal discharge fluid intake should be increased. |
CONSTIPATION
Difficulty in passing stool or passes once in 2 / 3 days, stools can be hard or soft is termed as constipation. Even ineffectual urge or a sensation of incomplete stools can be termed as constipation.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Do not suppress the urge to pass stools. |
COUGH
It is a violent exhalation to an irritant stimulus.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Treat the cause. |
CYSTINE STONES
KIDNEY STONES / URINARY CALCULI (CYSTINE STONES) :
The formation of crystals and calculi due to mineral deposits in urine are known as urinary calculi, when formed in kidney are known as kidney stones but can form any where in the urinary tract and they are named depending on the site where they are formed.
Cystine stones are formed from cystine, an amino acid that is found in protein. Less then 1% of kidney stones are made from cystine.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Kidney stones have tendency to reoccur, it can be prevented by some dietary changes. Depending upon the type of stones you can make necessary changes in your diet and prevent stone formation. |
D
DANDRUFF
Dry white flakes of skin, on your scalp is known as dandruff.
• It is not a health risk, but is a source of embarrassment.
• Some people have the wrong notion that it is because of bad hygiene or washing the hair often – this is a false belief. It is just that people having dandruff shed more skin then others.
• However some dermatologists suggest that is caused by a yeast fungus that is believed to breed in a combination of sebaceous oil and dead skin cells.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
DO: |
|
• Add one tea spoon of vinegar to the rinsing water after washing your hair. |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Drink plenty of water. |
DEPRESSION
Depression is a medical illness, which constitute feeling of hopelessness, feeling low with sadness and loss of interest in regular and social responsibilities. It affects the body, mood, and thoughts of the person.
|
DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Do`s: |
|
DON`TS: |
|
• Do not believe in your negative thoughts. |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Eat food in a relaxed atmosphere, as stress decreases the ability of our body to metabolize food. |
DIABETES OR JUEVENILE DIABETES
DIABETES / DIABETES INCIPIDUS / JUEVENILE DIABETES
It is a metabolic disorder in which utilization of blood glucose by the cells of the body is impaired, leading to high levels of glucose in blood and excessive excretion of glucose in the urine.
The main cause of high blood glucose levels in the body is decreased production of insulin (hormone produced by pancreas) or the body does not properly utilize insulin.
Normal glucose levels:
Fasting: 80 – 110 mg/dl.
Post meals up to 140 mg/dl.
Bed time glucose levels should be between 100 and 160 mg/dl.
|
DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Your blood sugar level in your blood is closely connected to what you eat, so good and balanced nutrition is most important for living a healthy life with diabetes. Correct choice of food and in appropriate amount will help you to control your blood sugar levels, thus further preventing or delaying the complications. There is no particular diet that will suit everyone; it depends on the treatment, individual sensitivity and on the complication of the disease. So consult your physician before implementing any diet plans. |
|
DO`S: |
|
• Follow your doctor`s instructions. |
|
AVOID: |
|
• Do not undertake strict diet to loose weight without consulting your physician or a registered dietician. |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• consume frequent small meals at regular intervals through out the day, instead of eating heavy meals once or twice a day. This will help to avoid extremes of high or low blood glucose levels. |
DIARRHEA OR DYSENTRY
DIARRHEA/ DYSENTRY
Diarrhoea is frequent passage of loose or watery unformed stools, commonly known as loose motions.
Large number of loose motions containing blood and mucus is called dysentery.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Drink plenty of fluids every 15-30 minutes. |
DYSPEPSIA AND INDIGESTION
Improper function of digestion is known as dyspepsia / indigestion.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Treat the cause. |
DYSPHAGIA
Difficulty in swallowing solids or liquids is called dysphagia.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Treat the cause. |
E
ECZEMA OR DERMATITIS
It is a chronic inflammatory condition of the skin causing a distinctive pattern of symptoms such as itching, scaling, thickening of skin and discoloration of skin.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
DO: |
|
• You can apply non-medicated ointments like petroleum jelly to soothe the irritation. |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Drink plenty of water. |
F
FLATULENCE
It is gas formation in stomach and intestine.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Go for a walk after meals, but not do brisk walking. |
G
GASTRITIS
Inflammation of the mucosa of the stomach.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• If possible fast for the day (do not eat for next 24 hrs). |
GASTROENTRITIS OR ENTERITIS [GASTROENTRITIS]
GASTROENTRITIS/ ENTERITIS
Inflammation of the stomach and intestine is known as gastroenteritis / enteritis
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Treat the cause. |
GINGIVITIS
Gingivitis is inflammation of gums.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Eat bland and soft food. |
H
HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA [HYPERCHOLESTROL]
It is an excess of cholesterol in the blood. It is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Avoid diet rich in saturated fats e.g. meat, eggs, milk products, cheese, butter etc. |
HYPERTENSION
Blood pressure which remains consistently high and not just once / twice is termed hypertension.
Blood pressure is measured in two parameters. One is systolic (upper) and second is diastolic (lower), 120/80 mm of mercury, is the normal reading. But a lot of doctors consider 140/90 mm of mercury within the normal range in young adults.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Cut down salt (common table salt) intake in your diet; do not exceed more then 2 to 2.5 gm a day. |
I
IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME [IBS]
Irritable bowel syndrome is more common in the age of 20-45 years.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• In acute phase of disease rest and take only liquids- water with salt and sugar, fruit juices- water melon, etc, start dioralyte in case of severe diarrhea. |
K
KIDNEY STONES OR URINARY CALCULI [URICACIDSTONE]
KIDNEY STONES / URINARY CALCULI (URIC ACID STONES):
The formation of crystals and calculi due to mineral deposits in urine are known as urinary calculi, when formed in kidney are known as kidney stones but can form any where in the urinary tract and they are named depending on the site where they are formed.
Uric acid – a waste product that normally passes out of the body in urine. About 10% of kidney stones are made of uric acid.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Kidney stones have tendency to reoccur, it can be prevented by some dietary changes. Depending upon the type of stones you can make necessary changes in your diet and prevent stone formation. |
M
MALNUTRITION
Inadequate supply of nutrients for body to function properly.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Increase intake of the nutrient you are deficient in. |
MIGRAINE
Migraines are vascular headaches with reoccurring throbbing pain usually affecting one side of the head.
Classification of migraine:
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
DO`S: |
|
• Keep a diary to record when your headache occurs, symptoms, what you had eaten before the headache started, your food craving that that period, your sleep patterns, menstrual cycle and other factors. This will help you to find out what triggers your migraine, so that you can avoid that factor and prevent migraine. |
P
PILES OR FISSURES OR FISTULA
PILES / FISSURES / FISTULA
Piles are caused by swollen veins inside or outside the anus.
Anal fissure is an elongated ulcer in the long axis of the lower anal canal.
Anal fistula is an abnormal passage formed rectum to the vagina.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Treat the cause. |
PNEUMONIA
An acute inflammation of the lung lining (parenchyma) is known as pneumonia.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Drink plenty of fluids and fresh juice of fruits and vegetables. |
PROTEIN ENERGY MALNUTRITION IN ADULTS [PEMA]
PEM (PROTEIN ENERGY MALNUTRITION) IN ADULTS
Protein Energy Malnutrition as the name suggests is lack of protein and energy resulting from poor nutrition.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Give high energy and high protein diet. |
PSORIASIS
Psoriasis is red scaly (silvery white) patches which can appear any where on the skin.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
DO: |
|
• Warmth may help to control relapses. |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Drink plenty of water. |
R
RENAL COLIC
Renal colic is pain in right or left lower abdomen or low back pain due to disease in the kidney, ureter or bladder.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• Drink plenty of fluids, 3-5 liters per day. |
RICKETS
It is the characteristic result of vitamin D deficiency in children.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• You should have sun bath for at least 1 – 2 hrs every day. |
S
SCURVY
Scurvy is due to vitamin C deficiency.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• In case of continues bleeding apply ice to stop bleeding. |
U
ULCERATIVE COLITIS [ULCERATIVECOLITIS]
Ulcerative colitis is due to inflammation of the rectum and the colon.
|
DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
• In acute phase of disease rest and take only liquids- water with salt and sugar, fruit juices- water melon, etc, start dioralyte in case of severe diarrhea. |
V
VITAMIN A DEFICIENCY
VITAMIN A DEFICIENCY / NIGHT BLINDNESS / XEROPTHALMIA
Deficiency of vitamin A.
Inability to see in dim light is known as night blindness (nyctalopia).
Xeropthalmia is an ocular manifestation of vitamin A deficiency.
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Increase intake of vitamin A: |
W
WERNICKES ENCEPHALOPATHY (KORSAKOFFS PSYCHOSIS) [KS]
WERNICKE`S ENCEPHALOPATHY (KORSAKOFF`S PSYCHOSIS)
It is a disease caused by deficiency of vitamin B1 (thiamine).
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Avoid: |
|
CONSUME: |
|
• Increase consumption of thiamine: |
Z
ZINC DEFICEINCY
Deficiency of zinc
| DIETARY MANAGEMENT: |
|
Consume: |
» BMI Interpritation
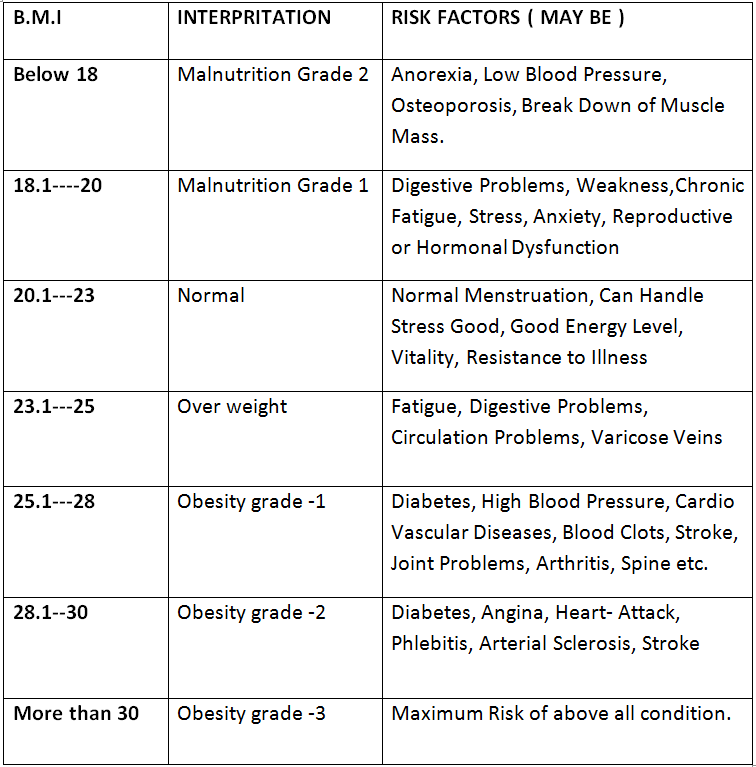
*TIPS TO LIVE HEALTHY:-
- TAKE SMALL BUT FREQUENT MEAL IT IMPROVES YOUR B.M.R.
- EAT SLOWLY AND CHEW PROPERLY WHICH IMPROVE YOUR DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
- TAKE 15-20 GLASS OF WATER WHICH PURIFY YOUR BODY
- DO 45 MINUITES ANY WORK OUT IN A DAY (WALKING/RUNNING/CYCLING/DANCING/SWIMMING/GYM EXERCISE)
- DO 15 MIN. REGULARLY YOGA/PRANAYAM/MEDITATION IT DECREASE YOUR STRESS LEVEL.
- BMR- BASAL METABOLIC RATE BMI- BODY MASS INDEX RDI- RECO. DIETARY INTAKE
(NOTE: ALL THE INFO. GIVEN ABOVE IS APROXIMATELY VALUE & BEST OF OUR KNOWLEDGE)









